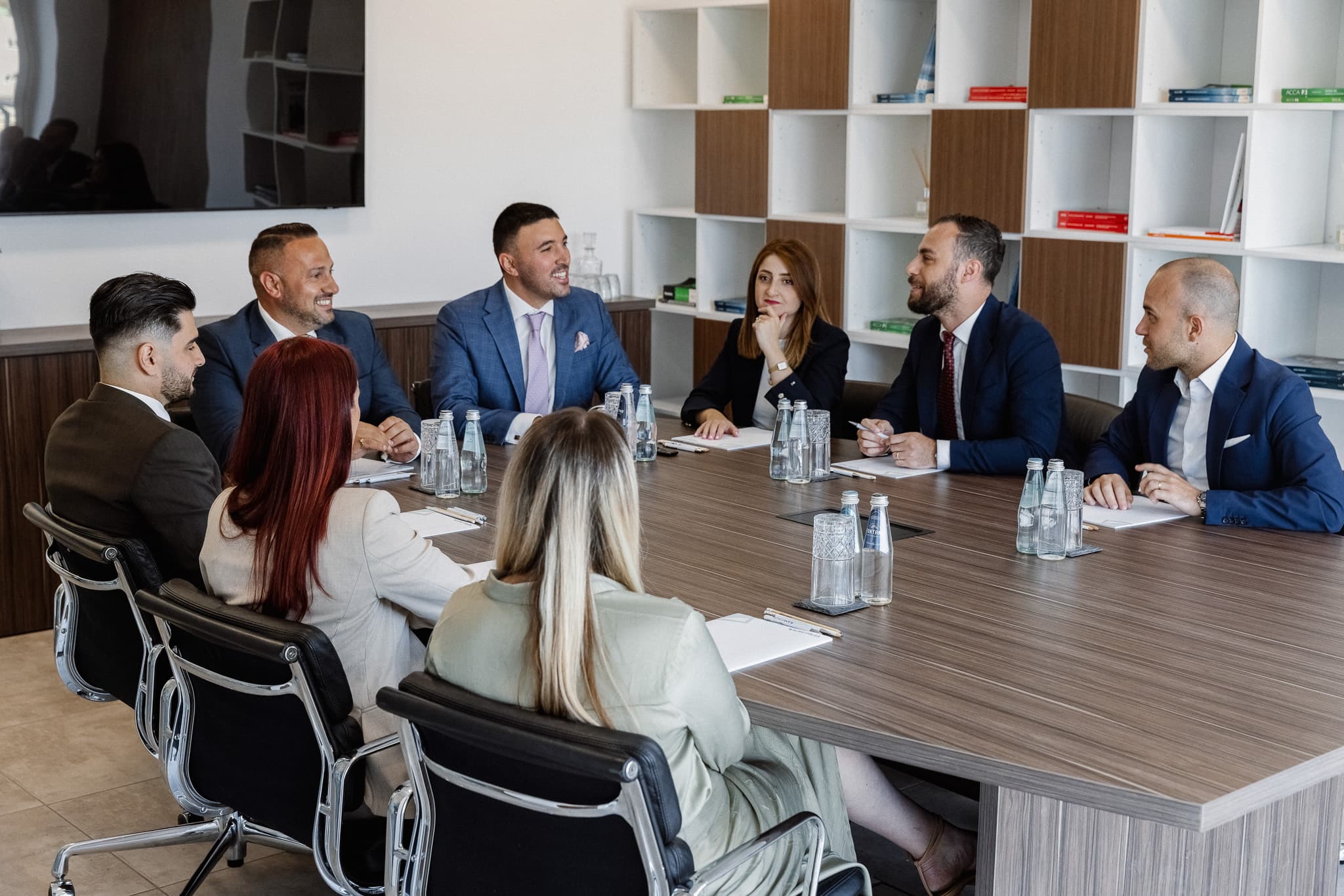
Leading Audit, Accounting & Tax Advisory Firm in Malta
Where Certified Expertise Meets Personalised Service
No fees. No obligations. Typically available within 48 hours.
Warranted by the Malta Accountancy Board
ACCA & MIA Certified Professionals
Corporate Member of FinanceMalta, MIT & IFSP
Fully GDPR & AMLD-Compliant
Some of our
Services
From audit and accounting to tax planning and regulatory compliance, our comprehensive suite of services ensures you that you receive expert, tailored and personalised support at every stage. Rather than forcing you into rigid, pre-packaged offerings, we take the time from the earliest stages of our communication to understand your specific requirements and goals, carefully considering key factors including industry dynamics, as well as your business growth ambitions. Whether you require a single specialist service or a complete bespoke financial assistant, we are committed to providing you with our professional support tailored to the specific needs of your business, not the other way around.
Accounting & Compliance
- Bookkeeping & Management Accounting
- Payroll Services
- VAT Compliance & Regulatory Reporting
Advisory & Corporate Services
- Company Formation & Secretary Services
- Start-up Support & Corporate Finance
- Business Restructuring, Liquidation & Malta Incorporation
- Bringing Companies in Good Standing
- Business Transformation & VIDA preparation

Regulated & Specialised Industries
- Remote Gaming Compliance
- Risk & AML Advisory
- Yacht Registration & Maritime Services
Tax & Structuring
- Malta Company Taxation & Tax Refunds
- Personal & Rental Tax (TA24) Returns
- Fiscal Consolidation & Holding Structures
Audit & Assurance
- Statutory and Special Audits
- EXO Number Applications & Financial Reports
- Audit Services for Gaming & Licensing
Get Expert Guidance for Your Business
Schedule Your Free Consultation
Why Leading Companies Place Their Trust in Us
Our clients choose us because they know we go beyond numbers to deliver results. When you partner with Borg Galea & Associates, you gain a team that genuinely cares about your success and takes the time to understand your unique industry challenges. With all services under one roof and our collaborative, client-centered approach, we make even the most complex challenges feel simple and manageable.
Save time
through streamlined processes and comprehensive, all-in-one solutions
Reduce costs
with competitive, transparent pricing and efficient service delivery
Simplify compliance
with proactive guidance, regulatory expertise, and timely updates
Experience responsive communication
that is honest, personal, and always accessible when you need it
Access full-service support
tailored to both local Maltese requirements and international business standards
Licenses & Qualifications
We are officially registered and recognised by relevant Maltese and international authorities. Our qualifications and licenses reflect our commitment to regulated, high-quality professional standards.








How we work
Our collaboration process is designed to be transparent, thoughtful, and client-centered – from the first contact to ongoing support.
Initial Contact & Consultation
You reach out with your needs – we respond quickly and schedule an introductory call to understand your goals and how we can help.
Internal Review & Strategic Planning
Our team assesses your situation, consults internally, and when needed, involves subject matter experts to craft a solution designed to meet your objectives.
Proposal & Clarification
We present a personalised proposal including service scope and pricing. Additional meetings may be held to ensure clarity and alignment.
Onboarding & Kick-Off
Upon acceptance, we guide you through a structured onboarding process, assign your service team, and define timelines and next steps.
Delivery, Communication & Follow-up
Our experts begin work with ongoing check-ins and full transparency. Once the engagement is complete, we review results and discuss future needs.
Not Sure Which Service You Need? We Can Help.
Speak with Our TeamAbout us
Borg Galea & Associates is your trusted partner for comprehensive financial, regulatory, and business advisory services. Founded on the principles of integrity, expertise, and genuine client partnership, we have built our reputation by consistently delivering exceptional results for businesses and individuals across diverse industries. Here is what drives our success and defines our identity.
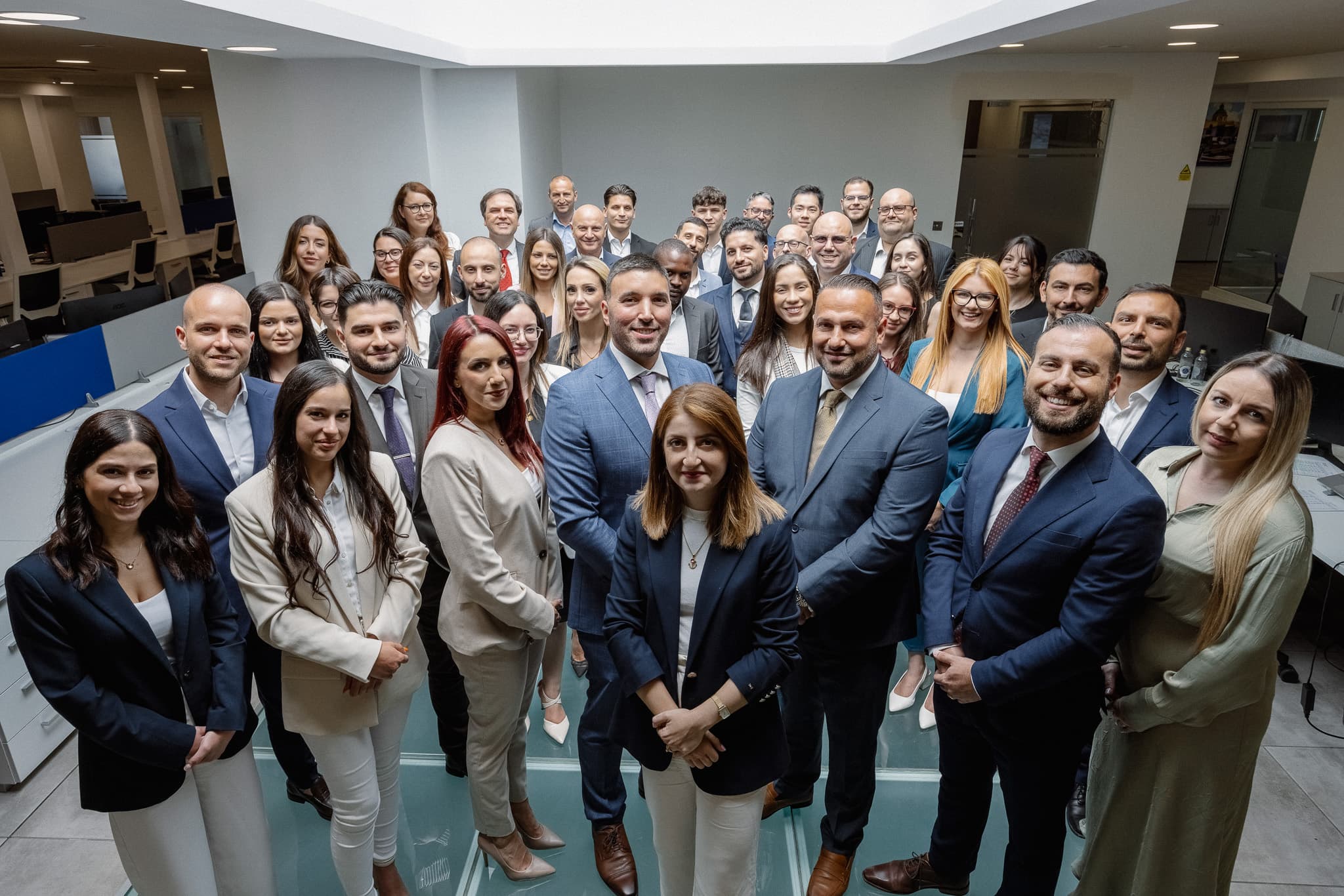


Our Beliefs Are Simple: Integrity Matters, and Transparency Builds Trust
We hold ourselves to the highest professional standards in everything we deliver, ensuring that clear communication and honest advice guide every interaction. This commitment has shaped a firm culture where we approach client relationships as true partnerships. We listen carefully, act responsibly, and always place the client's interest at the centre of everything we do.
Our team works as one and is built on mutual respect and continuous professional growth. Each member maintains relevant certifications and stays current with evolving regulations and industry best practices. This means our clients benefit from a collaborative, well-informed approach, rather than fragmented and outdated advice.
Whether you are a growing business, a multinational, or an individual navigating complex obligations, we treat every client with confidentiality, care, and long-term perspective.
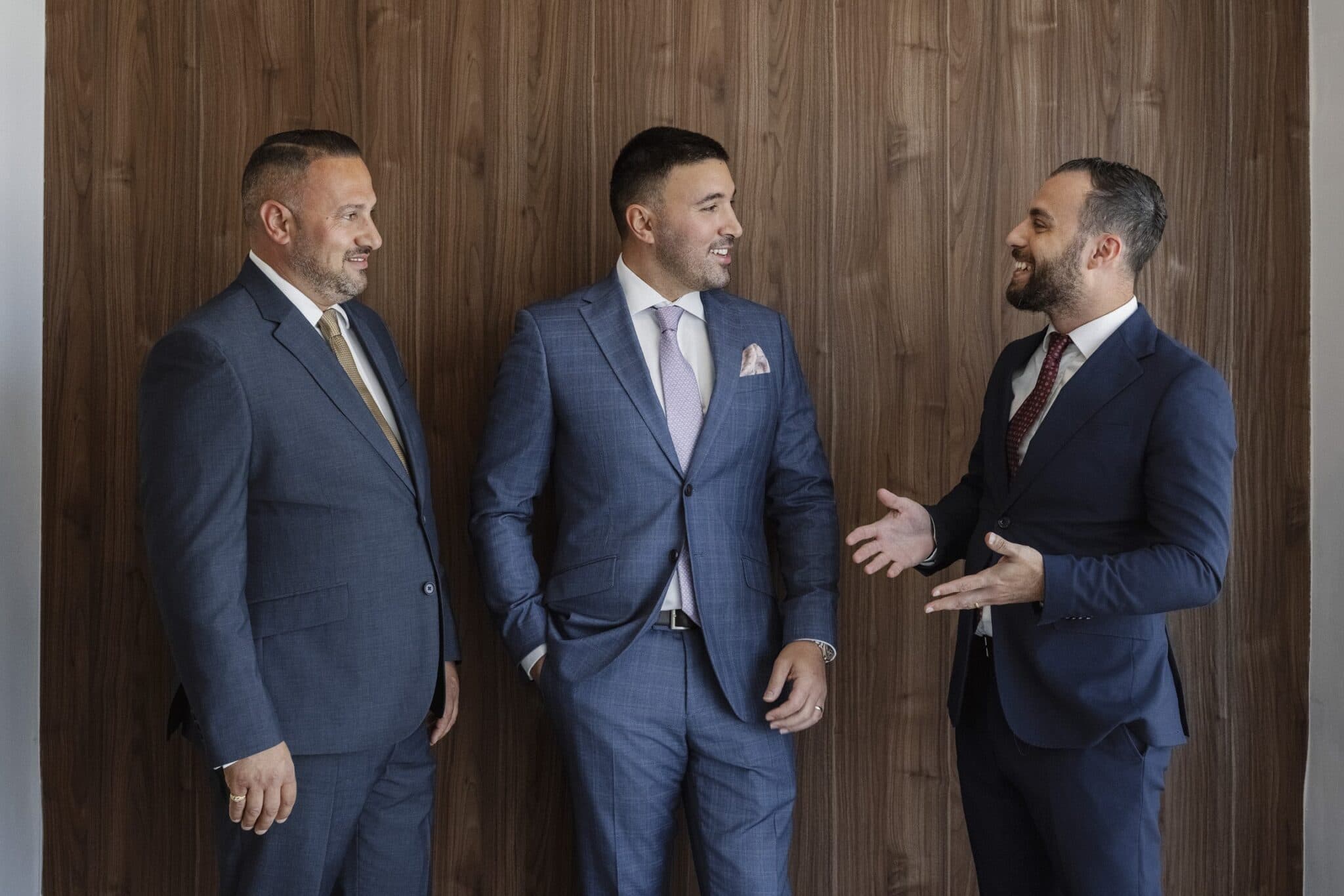


Our Promise
“We treat your goals as if they were our own – with integrity, clarity, and accountability at every step.”
Andrew Fenech
Business Development Manager
What Our Clients Say About Working With Us
At Borg Galea & Associates, we are proud to support clients from a wide range of industries and even prouder when they share their experience with us. Discover what they value most about working with our team.
Outstanding Service Quality, Always On Time
“Borg Galea & Associates have always managed to exceed our expectations in terms of quality of service. Very professional, friendly team who is always there to help. Reliable, meticulous in their work, and deliver on time. Highly recommended.”

Natalie Vella Wright,
Director – Billboard Connection
Long-Term Collaboration Built on Trust
“Borg Galea & Associates has been successfully supporting us in annual audits for several years. During our collaboration, we have only had positive experiences. In particular, the support from Nathaniel Borg was always characterized by quick and unbureaucratic help. Furthermore, a strong relationship of trust has built up, which ensures long-term cooperation.”

Matthias Keck
CEO & Founder – Devrock Ltd
Understanding Business Challenges Like No Other
“Working with Borg Galea & Associates has transformed the way we carry out our business activities, making our lives easier. The team helped us to understand our business, the challenges we faced and also assisted with how we can enhance our daily operations. We are pleased with their services in auditing, taxation and professional advisory, as well as their professional approach and high level of responsiveness. For sure we recommend the use of their services, and we are grateful to have Borg Galea & Associates to support us with our business growth.”

Renata Rukstelyte
Finance Executive - Sorens Aero
More Personal Than Other Larger Providers Out There
“I really enjoyed the process with Borg Galea & Associates, of whom I have been a client for the past few years. They work one-to-one with you to make sure your business receives the attention it requires. The whole team has always been prompt, professional and highly responsive. I would recommend anyone to use their services as it feels more personal than other larger providers out there. Big thanks and looking forward to keep on working with you in the future.”

Marcel Jaeger
Director - Infinium Digital Holdings
Trusted Partner for All Financial Matters
“I have been a client of Borg Galea & Associates for 5 years and have always found their services to be extremely professional and approachable. They support me through many financial tasks, both on a personal level and in respect of my company. They also enlist the help of other professionals to ensure that informed decisions are made. I highly recommend their services.”

Daniel Cutajar
Dino’s Motors
Outstanding Service Quality, Always On Time
“Borg Galea & Associates have always managed to exceed our expectations in terms of quality of service. Very professional, friendly team who is always there to help. Reliable, meticulous in their work, and deliver on time. Highly recommended.”

Natalie Vella Wright,
Director – Billboard Connection
Long-Term Collaboration Built on Trust
“Borg Galea & Associates has been successfully supporting us in annual audits for several years. During our collaboration, we have only had positive experiences. In particular, the support from Nathaniel Borg was always characterized by quick and unbureaucratic help. Furthermore, a strong relationship of trust has built up, which ensures long-term cooperation.”

Matthias Keck
CEO & Founder – Devrock Ltd
Get a Free Consultation
Submit your details below and one of our expert advisors will get back to you within 24 hours. No fees, no obligations.
You will speak with

Andrew Fenech
Business Development Manager
- Free initial consultation
- Response within 24 hours
- No obligations whatsoever
Publications & Insights

Keeping a Maltese Company in Good Standing
Read our latest guide about keeping a Maltese Company in good standing. Everything Malta business owners need to know about statutory obligations, filing deadlines, and avoiding penalties.
Explore the full guide
Chapter 6: Liquidation in Malta after Loss of Good Standing
Borg Galea and Associates
Overview: Introduction: Keeping a Maltese Company in Good Standing Chapter 1: Initial Steps and Obligations...
Read More →
VAT Treatment of Landlord Recharges
Borg Galea and Associates
In practice, it is common for landlords to recharge tenants for expenses such as water...
Read More →
VAT Registrations
Borg Galea and Associates
Company officers must remain vigilant of their obligation to register for VAT purposes in Malta...
Read More →Careers - Join Our Growing Team
We are always looking for driven, talented professionals to grow with us.
Join a team that is expanding with purpose and discover a supportive environment where your contributions are valued and your career aspirations are taken seriously.
If you thrive in a collaborative culture where integrity guides every decision and where helping clients succeed gives you genuine satisfaction, we want to hear from you.